Reciprocating Compressor
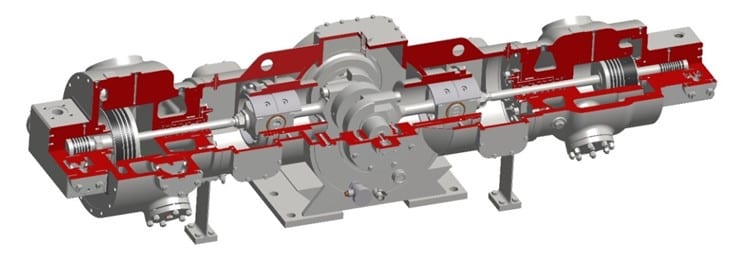
Similar to an automotive combustion engine, except passive non return valves replace actuated valves.
A piston travels up and down inside a cylinder, and is connected to a crank shaft by a connecting rod.
On the intake stroke, the discharge valves are forced shut, and gas is therefore sucked into the cylinder.
On the compression stroke the suction valves are forced shut, and gas is expelled into the discharge port.
On multi-stage machines, the gas must be cooled before entering the next stage.
| Typical Performance Envelope | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Advantages | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Disadvantages | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common Applications | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
